- Home
Blog Blog
Payments Resources Payments Resources
Payment Gateway Features: the Pros & Cons of Different B2B Payment Methods
Payment Gateway Features: the Pros & Cons of Different B2B Payment Methods

Having a multitude of different payment methods is vastly advantageous to the discerning digital merchant as compared to sticking with a single payment method.
For B2B payment platforms, having a variety of payment methods matters because it not only helps in garnering a positive experience amongst local and international users, but also decreases checkout abandonment. The reason for this is because having multiple payment methods not only improves the user experience since some users are bound to be sticky about using one payment method over the other, but it also helps in learning about the current globally available payment methods to make an informed decision about which payment gateway you wish to use for your B2B checkout.
This is especially useful when thinking about localising your business in a given market or globalising your business since getting the right tool for the right job can make the difference between middling profits and incredible gains.
Given that the 2020 estimate of the global market value of online B2B transactions was 14.9 trillion USD, which would make it 5 times larger than that of its B2C counterpart, it is therefore more important than ever for B2B merchants and service providers alike to keep abreast of the types of payment methods available that suits their business needs¹.
Payment methods for B2B payment platforms can be categorised into two distinct categories: localised methods and international methods.
Marketplaces, SaaS platforms, exporters & importers, and service providers. No matter your business needs, Omoney has a payment solution for you! Collect payments in over 173 countries and localise in over 70 key markets with only one account! Contact us today!
Localised Payment Methods
Localised payment methods are payment methods that are typically available when the payment platform being utilised is integrated with local payment providers in the region where the buyer is at and/or has a local account. They are crucial for any business looking to localise in any given market to consider since they go a long way in building up trust and reputation with the local populace and establishing the credibility of a business’ brand. Here are a couple of the common localised methods for conducting payments:
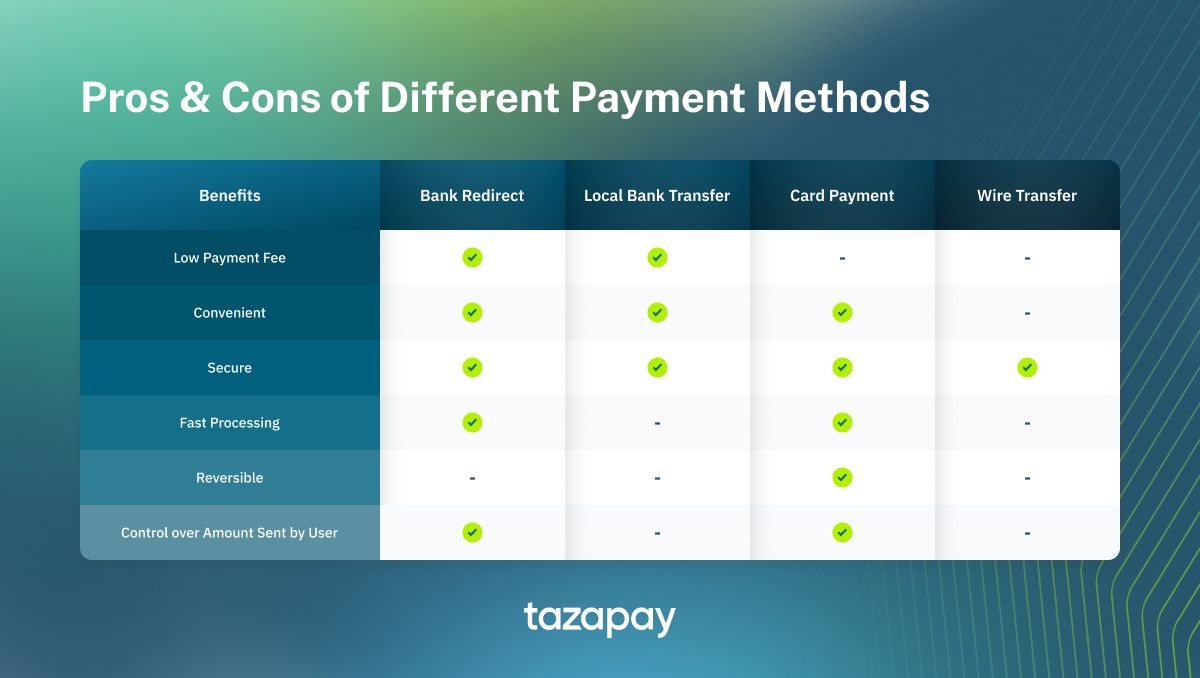
Bank Redirect
Bank redirects, as the name suggests, allow customers to pay online with their bank accounts by redirecting them to the online banking portal of their chosen bank. There, they can login to their bank accounts and make payments accordingly.
They are commonly used by retailers in Europe and Asia-Pacific that are looking to improve conversion rates and reduce fraud with customers, and service businesses or software collecting one-time payments (OTPs) from other businesses. Half of all online commerce in Germany, the Netherlands, and Malaysia are driven by bank redirects. Common entry points for bank redirects include linked buttons in checkout or QR codes as seen in Singapore’s Paynow QR and India’s United Payments Interface or UPI.
The pros and cons of bank redirects are as follows:
Pros
- Low payment adoption fees
- High brand trust especially when integrated with local banks
- Easier cash flow due to instant settlement
- Payment accuracy is ensured as the amount paid is controlled by data shared between the vendor and the payment platform’s checkout to the bank account
Cons
- Heavily reliant on bank server-side reliability and internet connectivity
- Payment is irreversible for the buyer. Any disputes need to be settled via the payment platform itself
Local Bank Transfer
Local bank transfers are a safe and reliable way for customers to send money over bank rails, often times faster than SWIFT/wire transfers. Being readily available in virtually any country with a decent banking system, it is easily accessible to most customers and usually popular in markets where the penetration rate for the more recent payment methods such as QR codes are relatively low such as Malaysia, Thailand, and Singapore².
They allow customers to input their bank account details to make an asynchronous transfer from checkout and usually the bank account details used are the payment platform’s. Users then have to show proof that the transfer has been made to the payment platform.
The advantages and disadvantages of this methods are as follows:
Pros
- Low payment fees
- High brand trust
- Bank rails are usually reliable, being separate from any integration-related dependencies
Cons
- Longer lead time since the payment platform needs to manually verify the payment receipt
- No control over amount of money sent, user may over or under pay by mistake
- Irreversible. The payment platform needs to intervene if mistakes and/or disputes are made.
International Payment Methods
International methods refer to payment methods offered by a payment platform in the event where it has yet to integrate with a local bank within the buyer’s country and/or the buyer makes the payment from a region outside the payment platform’s scope of localisation. These methods are referred to as such due to their capability to make payments from anywhere in the world that supports them. Some of these payment methods are:
Card Payments
Card payments are easily one of the most common methods used for online purchases the world over, boasting a high penetration rate in most countries. In Southeast Asia alone, the penetration rate for cards can range anywhere between 22% and 75%, with the highest being Singapore². Because of this ubiquity, they are readily available as both an international payment method and a localised payment method.
Pros
- Payments are secured via 3DS, the e-commerce authentication protocol for card payments³
- Convenient
- Instant payment, easing up cash flow
Cons
- Chargeback risk from fraudulent buyers. They have a high rate of occurrence in the US and Canada where the chargeback ratios reported for the countries are 1.5% and 3.57% respectively⁴.
- Higher transaction fees than non-card rails
Wire Transfer
Wire transfers refer to the electronic transfer of money that operates on a number of networks, most famously SWIFT⁵. Much like card payments, they can also be utilised as an international payment method and a localised payment method.
Pros
- One of the most trusted international payment rails, guaranteed with trustworthy networks such as SWIFT
- More secure compared to international bank transfers
- Globally available
Cons
- Irreversible
- No control over amount sent by user
- High processing fee⁶
- Take longer to process than card payments
Now that you know more about the benefits and disadvantages of different payment methods for B2B payment platforms, you can now make a better informed decision the next time you wish to choose a payment method for your business needs. While you’re at it, have a look into Omoney. With one account, you can tap into over 173 different markets and easily localise into more than 70 key markets with their fully digital payment solutions that can be tailored for your specific needs.
Sources
- In-depth Report: B2B e-Commerce 2021 | Statista
- E-Commerce Payment Trends in Southeast Asia | Fintech Singapore (fintechnews.sg)
- What Is SSL (Secure Sockets Layer)? | What is an SSL Certificate? | DigiCert
- Chargeback Report: Rates, Statistics & Analysis | MIDIGATOR
- What Is A Wire Transfer? – Forbes Advisor
- Wire Transfers: How It Works? Pros and Cons of Wiring - ACE Money Transfer
Category

Payments Resources
Payment Gateway Features: the Pros & Cons of Different B2B Payment Methods
Related Articles

Local Payment Methods in Indonesia: How Dana Works in an International Payment Gateway







