- Home
Blog Blog
Payments Resources Payments Resources
Local Payment Methods: How Africa’s Mobile Money Checkout Works in an International Payment Gateway
Local Payment Methods: How Africa’s Mobile Money Checkout Works in an International Payment Gateway

The global digital marketplace is one that is ever-changing and rapidly growing with each passing moment. Chief among these is mobile money transactions, which themselves comprise about $1 trillion dollars in value around this year¹. More interestingly, as of this May, Africa now accounts for 70% of that incredible mobile money value¹. Given the continent’s small yet quickly growing banked population, going from 171 million to 456 million from 2012 till 2022, it is apparent that the adoption of mobile money payments is instrumental to this unparalleled growth in mobile money value despite the massive unbanked population². That being said, what is Mobile Money, and how does it work?
Eager to grow your business but unsure where to expand to? Why not choose a digital payment platform that allows you to choose virtually any market in the world! With Omoney, experience seamless borderless payments as over 173 markets are now yours to pick and choose from. We also offer a selection of up to 84 localised markets at your disposal. Interested? Contact us today.
What is Mobile Money?
Mobile Money is a digital payment platform and alternative payment method that allows users to transfer money between cellphone devices without the need to be connected to the formal banking system, distinguishing them from mobile banking-based payment methods where they would normally manage their funds in their bank accounts via Internet-connected mobile devices³. A major factor in this distinction is the fact that mobile money payments are usually powered by telecommunications companies or telcos, as opposed to formal banking institutions though some African countries have bank-led mobile money initiatives such as Nigeria⁴.
This characteristic of mobile money payments makes them akin to e-wallets, since the user stores and manages their funds in a secure electronic account that is linked to their phone number⁵. Cash withdrawals are also possible with mobile money if carried out at authorised agents⁵.
How Does it Work in Checkout?
Checkout with mobile money payments are almost identical to that of most electronic wallets’, in the sense that both involve either redirecting users to the necessary payment page to conduct their funds transfer after they’ve confirmed what they wanted to buy. However, as its name suggests, the buyer would need to input their mobile number as a mandatory field for the required payment details since their funds are linked to them. Once they are filled in along with the correct amount intended to be transferred, the checkout process is finalised and the funds are summarily transferred.
Why is Mobile Money Popular in Africa?
Mobile Money’s inherent popularity in Africa can be attributed to it being powered by telcos as opposed to formal banking institutions, allowing the platform to penetrate deeply into low resource settings with greater ease than their conventional payment counterparts⁶. Considering the fact that as of this year, 57% of the region’s total population lacks any form of bank account, being able to conduct transactions without the need for a bank account would increase the payment method’s appeal exponentially to the unbanked demographic⁶. As for the banked remainder which is made of the aforementioned 456 million, 40% of them prefer digital channels for transactions, thereby making mobile money transactions suited for them as well.
It also helps that there are both regional and pan-African providers for mobile money transactions across the various nations in the continent. These include AirtelTigo in Ghana, Tigo Tanzania in Tanzania, and M-PESA, a Vodafone and Safaricom subsidiary operating in 9 African countries.
The world is now your market - unlock local payment methods for your eCommerce website using our API integration. Wanna know more? Find out here:
Benefits and Drawbacks of Mobile Money for International eCommerce
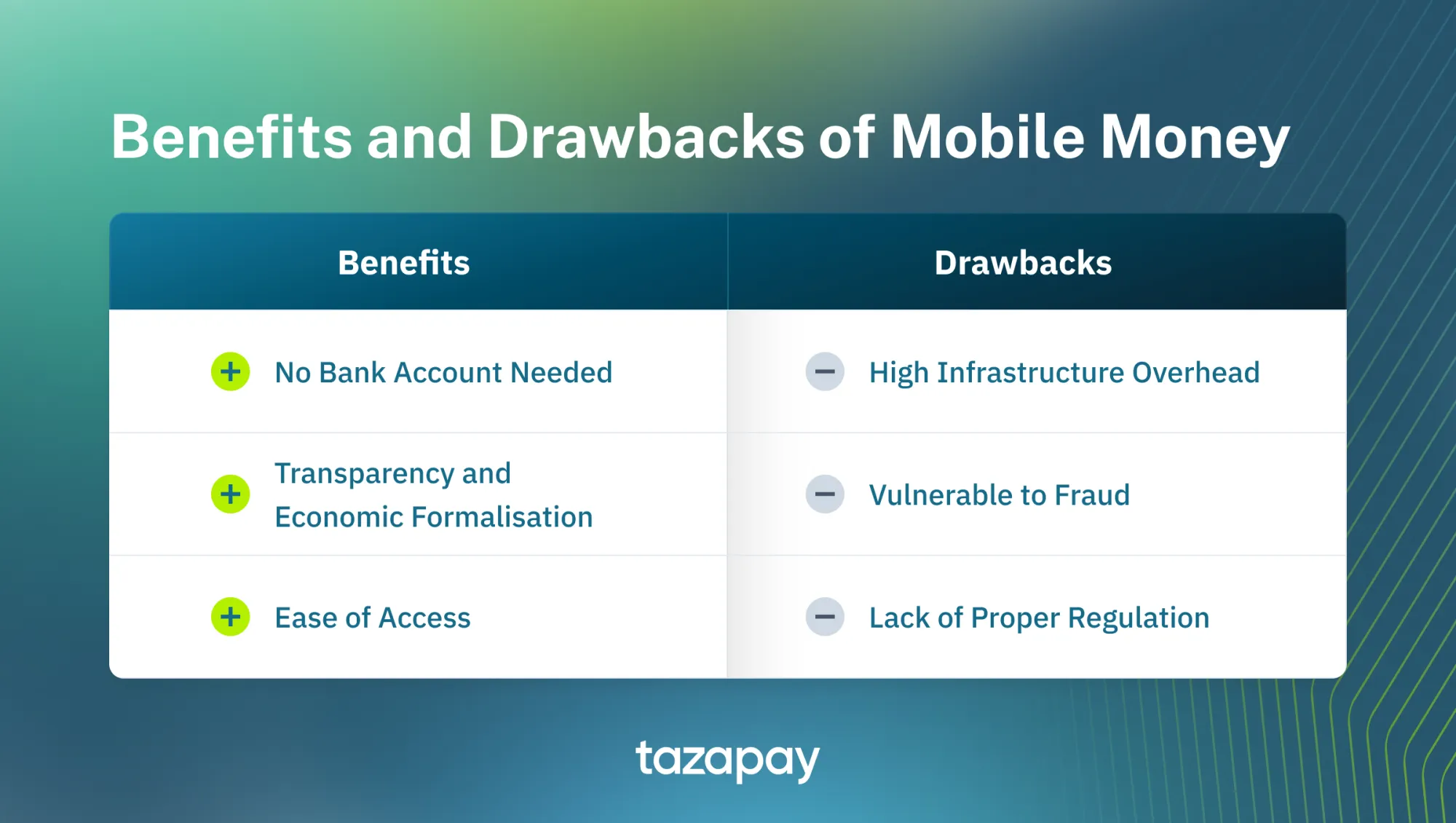
Like any other payment method, there are benefits and drawbacks to Mobile Money. They are as follows:
Benefits
- No Bank Account Needed: Mobile Money effectively being an electronic wallet allows users to transfer and manage funds through an account linked with their phones rather than their bank accounts, making it accessible to the unbanked.
- Transparency and Formalisation of Economy: All transactions are recorded in mobile money transactions, improving payment security and making them more transparent at the same time. This increase in transparency would also improve tax collection significantly, and could open the path towards integrating informal sector users into the formal banking system, thereby increasing the conversion towards the banked population.
- Ease of Access: Users only require a valid mobile number, a phone, and access to the internet in order to make transactions, whether it be B2C, B2B, or P2P.
Drawbacks
- Infrastructure Challenges: Mobile Money being powered by telcos also mean that they are heavily reliant on the spread and reach of the infrastructure of these telcos, which often require significant up-front investment to provide. Moreover, most Mobile Money services are reliant on SMS-based technology, creating a compatibility issue when attempting to link with other internet-based digital financial products.
- Operational Risks: While the fact that they record all transactions may make it more secure, it still is vulnerable to fraud and data breaches, especially if the mobile money companies fail to properly encrypt communications.
- Regulatory Challenges: Despite its popularity and relative ubiquity in the continent, it is still fairly young, leading to most policymakers and private companies struggling to come up with ideal solutions to regulating mobile money against its operational risks.
If you were looking to expand your business into Africa, then you now know more about Mobile Money payments and how you can capitalise this information to your advantage. Improve your chances further with a payment platform that offers mobile money transactions as a localised payment method, such as Omoney. They have operations in over 173 countries the world over and have an impressive selection of over 84 localised markets to choose from. Still not convinced? Why not try them out today and see for yourself!
Sources
- GSMA: 70% of the world's $1 trillion mobile money market is in Africa — Quartz Africa (qz.com)
- Number of banked adults in Africa 2012-2022 | Statista
- The Rise of Mobile Money in Sub-Saharan Africa: Has the Digital Technology Lived up to its Promise? | African Arguments
- Financial inclusion in Nigeria: mobile money services, payment services, banks and telecoms operators | International Bar Association (ibanet.org)
- How do mobile money payments work? (worldremit.com)
- 57% of Africa’s population lacking any form of bank account - https://middleeast-business.com
Category

Payments Resources
Local Payment Methods: How Africa’s Mobile Money Checkout Works in an International Payment Gateway
Related Articles

Local Payment Methods in Indonesia: How Dana Works in an International Payment Gateway







